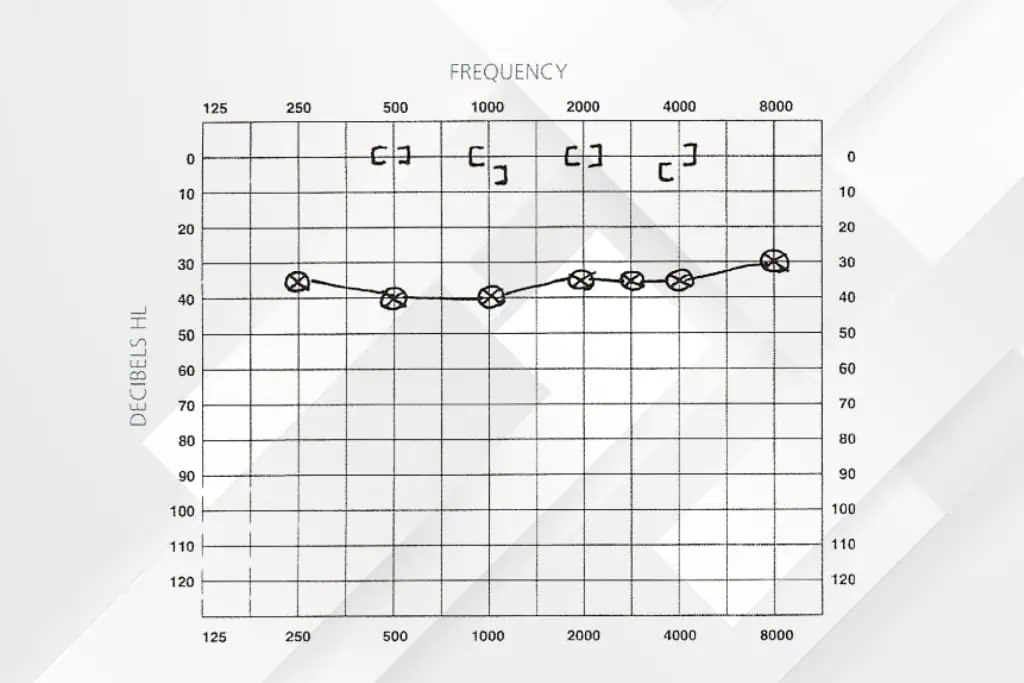
What is Sensorineural Hearing Loss?



Sensorineural hearing loss is a hearing loss due to damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve which makes hearing sounds transmitted to the brain impossible. This type of hearing loss is often permanent and is commonly caused by several factors: age, noise exposure, and genetics.
Sensorineural hearing loss can occur in one ear or both, from mild sensorineural hearing loss to moderate or even bilateral sensorineural hearing loss when both ears are involved.